About Ectopic Pregnancy
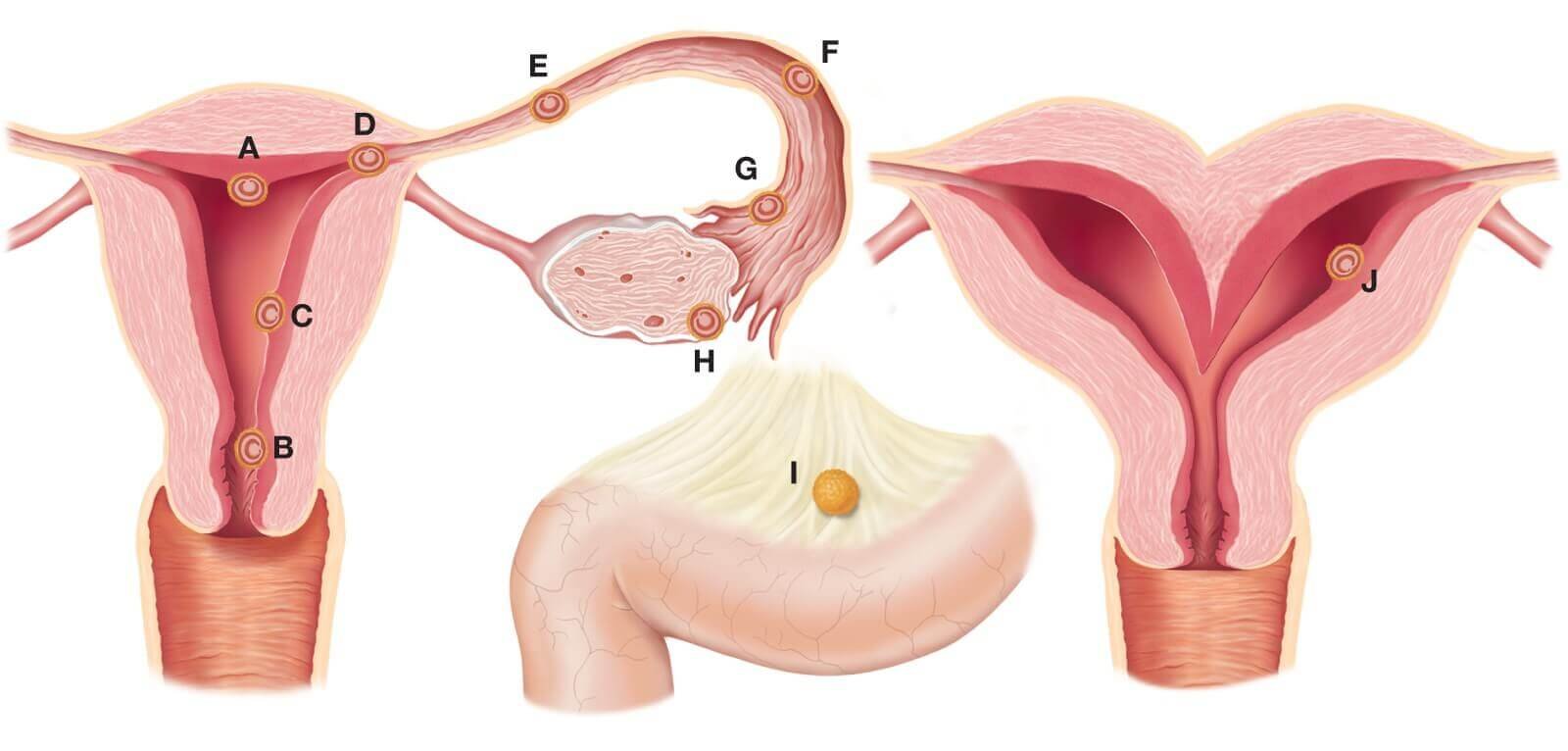
In a normal pregnancy, the fertilized egg implants and develops in the uterus. In most ectopic pregnancies, the egg settles in the fallopian tubes. This is why ectopic pregnancies are commonly called “tubal pregnancies.” The egg also can implant in the ovary, abdomen, or the cervix, so you also might hear these referred to as cervical or abdominal pregnancies.
None of these areas has as much space or nurturing tissue as a uterus for a pregnancy to develop. As the fetus grows, it will eventually burst the organ that contains it. This can cause severe bleeding and endanger the mother’s life. A classical ectopic pregnancy does not develop into a live birth.
For pregnancy to happen, the ovary has to release an egg into the fallopian tube, where it stays for about 24 hours. There it has to come in contact with a sperm to be fertilized. The fertilized egg stays in the fallopian tube for 3 or 4 days before it heads to the uterus. There it attaches to the lining and continues to grow until a baby is born.
But if the fertilized egg implants in your fallopian tube or somewhere else in your abdomen, you end up with what’s called an ectopic pregnancy. In these cases, the pregnancy can’t continue normally, and it requires emergency treatment.
Symptoms
Ectopic pregnancy can be difficult to diagnose because symptoms often are like those of a normal early pregnancy. These can include missed periods, breast tenderness, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, or frequent urination (peeing).
Often, the first warning signs of an ectopic pregnancy are pain or vaginal bleeding. There might be pain in the pelvis, abdomen, or even the shoulder or neck (if blood from a ruptured ectopic pregnancy builds up and irritates certain nerves). The pain can range from mild and dull to severe and sharp. It might be felt on just one side of the pelvis or all over.
Any of these symptoms also might happen with an ectopic pregnancy:
- vaginal spotting
- dizziness or fainting (caused by blood loss)
- low blood pressure (also caused by blood loss)
- lower back pain
Most of the time, an ectopic pregnancy happens within the first few weeks of pregnancy. You might not even know you’re pregnant and may not have signs of a problem.
Light vaginal bleeding and pelvic pain are usually the first symptoms, but others could include:
- Nausea and vomiting with pain
- Sharp abdominal cramps
- Pain on one side of your body
- Dizziness or weakness
- Pain in your shoulder, neck, or rectum
Nausea and breast soreness are common symptoms in both ectopic and uterine pregnancies. The following symptoms are more common in an ectopic pregnancy and can indicate a medical emergency:
- sharp waves of pain in the abdomen, pelvis, shoulder, or neck
- severe pain that occurs on one side of the abdomen
- light to heavy vaginal spotting or bleeding
- dizziness or fainting
- rectal pressure
You should contact your doctor or seek immediate treatment if you know that you’re pregnant and have any of these symptoms.
Ectopic pregnancy can lead to fallopian tube rupture. If that happens, you could have major pain with or without severe bleeding. Or the bleeding could be internal. Call your doctor immediately if you have heavy vaginal bleeding that causes lightheadedness, fainting, or shoulder pain, or if you have any severe abdominal pain, especially if it is on one side of the belly.
Emergency symptoms
If the fertilized egg continues to grow in the fallopian tube, it can cause the tube to rupture. Heavy bleeding inside the abdomen is likely. Symptoms of this life-threatening event include extreme lightheadedness, fainting, severe abdominal pain, and shock.












No comments:
Post a Comment